Partial Knee Replacement Surgery
Partial knee replacement surgery is a procedure designed to remove a single part of a damaged knee. This can include damaged tissue or cartilage within the knee joint that is preventing proper functionality. The defective components of the knee will be replaced with artificial implants. Patients who require this procedure typically have arthritis present in only part of their knee.
At Barrington Orthopedic Specialists, our experienced, certified knee specialists can perform partial knee replacement surgery, designed to remove damaged components of the knee while preserving range of motion and knee function. Our team will work alongside you at every step of your surgery and help you to develop a personalized rehabilitation plan that will ensure a quick and healthy recovery.
If you’re struggling with knee pain, we are here to provide you with relief. Schedule your first consultation with the team at Barrington Orthopedic Specialists today. If you’re in an emergency situation, visit the Immediate Care Clinic at our Schaumburg, IL location.
What Is A Partial Knee Replacement?
The goal of knee replacement surgery is to decrease pain and restore function. Although total knee replacement (also called “arthroplasty”) is an excellent option for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee, other surgical options exist.
Patients with osteoarthritis that is limited to just one part of the knee may be candidates for unicompartmental knee replacement (also called a “partial” knee replacement).
Unicompartmental knee replacement is an option for a small percentage of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.
Your orthopedic doctor may recommend partial knee replacement if your arthritis is confined to a single part (compartment) of your knee.
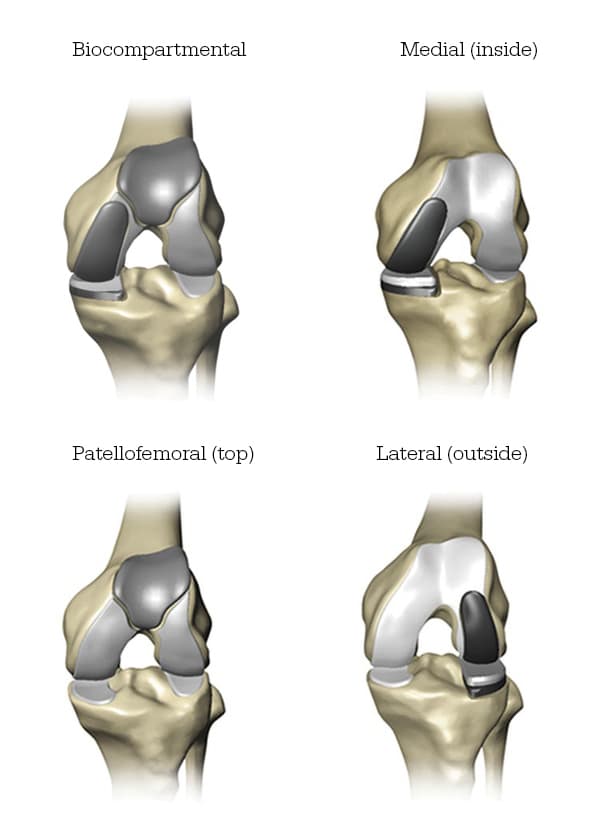
Your knee is divided into three major compartments: The medial compartment (the inside part of the knee), the lateral compartment (the outside part), and the patellofemoral compartment (the front of the knee between the kneecap and thighbone).
In a unicompartmental knee replacement, only the damaged compartment is replaced with metal and plastic. The healthy cartilage and bone in the rest of the knee is left alone.
Advantages of Partial Knee Replacement
Multiple studies have shown that modern unicompartmental knee replacement performs very well in the vast majority of patients who are appropriate candidates. The advantages of partial knee replacement over total knee replacement include:
- Quicker recovery
- Less pain after surgery
- Less blood loss
- Also, because the bone, cartilage, and ligaments in the healthy parts of the knee are kept, most patients report that a unicompartmental knee replacement feels more “natural” than a total knee replacement.
- A unicompartmental knee may also bend better.
Partial Knee Replacement
A partial knee replacement operation typically lasts between 1 and 2 hours.
Your surgeon will make an incision at the front of your knee exploring the three compartments of your knee to verify that the cartilage damage is, in fact, limited to one compartment and that your ligaments are intact.
If your surgeon feels that your knee is unsuitable for a partial knee replacement, he or she will instead perform a total knee replacement.
He or she will discuss this contingency plan with you before your operation to make sure that you agree with this strategy.
If your knee is suitable for a partial knee replacement, your surgeon will use special saws to remove the cartilage from the damaged compartment of your knee and will cap the ends of the femur and tibia with metal coverings. The metal components are generally held to the bone with cement. A plastic insert is placed between the two metal components to allow for a smooth gliding surface.
Mako for Partial Knee replacement
We understand that knowing what to expect from your joint replacement experience is important to you. As you are reading through this material, please reach out to us to discuss if you have additional questions.
Each patient is unique and can experience joint pain for different reasons. It’s important to talk to us about the reason for your knee pain so you can understand the treatment options available to you. Pain from arthritis and joint degeneration can be constant or come and go, occur with movement or after a period of rest, or be located in one spot or many parts of the body. It is common for patients to try medication and other conservative treatments to treat their knee pain. If you haven’t experienced adequate relief with those treatment options, you may be a candidate for Partial Knee replacement, which may provide you with relief from your knee pain.
Mako can help your surgeon plan for better outcomes, like less pain and shorter recovery times compared to manual partial knee replacement surgery.
How Mako works

The MAKO system is an advanced, surgeon-controlled, robotic arm designed to increase the accuracy of knee replacements. Mako is an innovative solution for many suffering from painful arthritis of the knee.
Scan. It all starts with a CT scan so your surgeon can know more about your anatomy.
Plan. The CT scan is used to create a 3D CT-based model of your knee. Your surgeon uses this 3D model to create a personalized surgical plan and assist your surgeon in performing your knee replacement procedure.
Mako Can. In the operating room, your surgeon follows your personalized surgical plan while preparing the bone for the implant. The surgeon guides Mako’s robotic arm within the predefined area, and Mako’s AccuStopTM technology helps the surgeon stay within the planned boundaries that were defined when the personalized preoperative plan was created.
It's important to understand that the surgery is performed by an orthopaedic surgeon, who guides Mako's robotic arm during the surgery to position the implant in the knee joint. Mako does not perform surgery, make decisions on its own or move without the surgeon guiding it. Mako also allows your surgeon to make adjustments to your plan during surgery as needed.
- Mako for Partial Knee replacement(opens in a new tab) is a treatment option for adults living with early to mid stage osteoarthritis (OA) that has not yet progressed to all three compartments of the knee. Depending on where the arthritis affects the knee, patients may have an implant inserted in any of the following areas:
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Partial knee replacement
Knee replacement is intended for use in individuals with joint disease resulting from degenerative and rheumatoid arthritis, or avascular necrosis.
Knee joint replacement is intended for use in individuals with joint disease resulting from degenerative, rheumatoid and post- traumatic arthritis, and for moderate deformity of the knee.
Joint replacement surgery is not appropriate for patients with certain types of infections, any mental or neuromuscular disorder which would create an unacceptable risk of prosthesis instability, prosthesis fixation failure or complications in postoperative care, compromised bone stock, skeletal immaturity, severe instability of the joint, or excessive body weight.
Like any surgery, joint replacement surgery has serious risks which include, but are not limited to, pain, infection, bone fracture, change in the treated leg length (hip), joint stiffness, hip joint fusion, amputation, peripheral neuropathies (nerve damage), circulatory compromise (including deep vein thrombosis (blood clots in the legs)), genitourinary disorders (including kidney failure), gastrointestinal disorders (including paralytic ileus (loss of intestinal digestive movement)), vascular disorders (including thrombus (blood clots), blood loss, or changes in blood pressure or heart rhythm), bronchopulmonary disorders (including emboli, stroke or pneumonia), heart attack, and death.
Implant related risks which may lead to a revision of the implant include dislocation, loosening, fracture, nerve damage, heterotopic bone formation (abnormal bone growth in tissue), wear of the implant, metal and/or foreign body sensitivity, soft tissue imbalance, osteolysis (localized progressive bone loss), audible sounds during motion, reaction to particle debris , and reaction to metal ions (ALTR). Hip and knee implants may not provide the same feel or performance characteristics experienced with a normal healthy joint.
The information presented is for educational purposes only. Speak to your doctor to decide if joint replacement surgery is appropriate for you. Individual results vary and not all patients will return to the same activity level. The lifetime of any joint replacement is limited and depends on several factors like patient weight and activity level. Your doctor will counsel you about strategies to potentially prolong the lifetime of the device, including avoiding high-impact activities, such as running, as well as maintaining a healthy weight. It is important to closely follow your doctor’s instructions regarding post-surgery activity, treatment and follow-up care. Ask your doctor if a joint replacement is right for you.
Stryker Corporation or its other divisions or other corporate affiliated entities own, use or have applied for the following trademarks or service marks: AccuStop, Mako, Stryker, Triathlon. All other trademarks are trademarks of their respective owners.
References
- Kayani B, Konan S, Tahmassebi J, Rowan F, Haddad F. An assessment of early functional rehabilitation and hospital discharge in conventional versus robotic-arm assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: A PROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY Bone Joint J 2019;101-B:24–33
JR-MKOSYM-OTHW-747688
Copyright © 2023 Stryker